Understanding the Equine Patella: Anatomy and Function
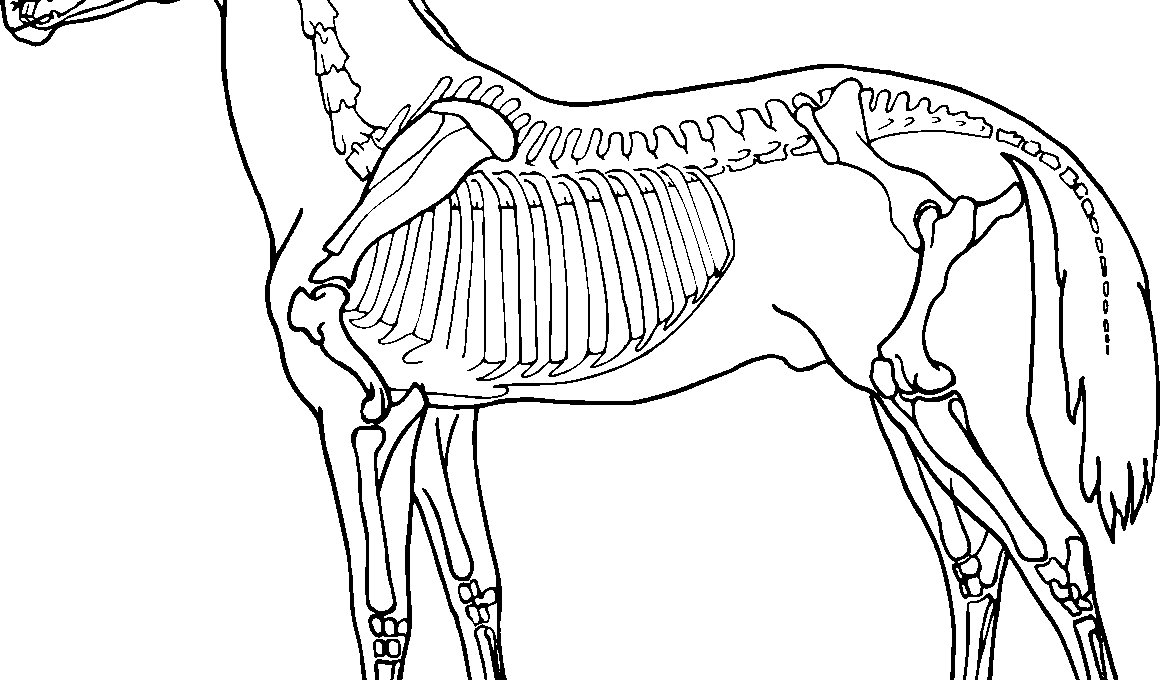
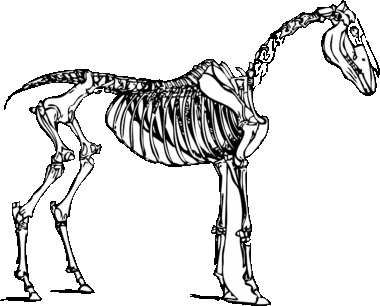
The equine patella is a critical component of a horse’s leg anatomy, playing a significant role in its movement and functionality. Located in the stifle joint, the patella, commonly referred to as the kneecap, provides stability and aids in the overall mechanics of locomotion. Understanding the structure of the patella is essential for horse owners, trainers, and veterinarians. It helps to recognize potential injuries that might occur. The horse’s patella consists of several important features, including its articular surfaces and the ligaments associated with it. The patella’s position in the stifle allows it to glide smoothly over the femur as the horse flexes and extends its leg. This sliding mechanism facilitates efficient movement, particularly during activities such as jumping, trotting, and galloping. The patella also helps protect underlying structures from wear and tear. In addition, the structure’s alignment can impact the horse’s performance, including its ability to pivot and maintain speed. Understanding the function of the equine patella aids in the overall care, training, and rehabilitation processes for these magnificent animals.
The equine patella consists of a bony structure that articulates with the femur at the stifle joint, creating a critical interface during movement. The patella serves as a fulcrum, enhancing the efficiency of the quadriceps muscle group. The primary function of the patella is to facilitate smooth movement between the femur and tibia by maintaining proper alignment. In horses, this alignment is crucial as it directly impacts performance and overall health. When the horse extends its leg, the patella stabilizes the stifle, allowing other muscles and tendons to perform optimally. The anatomy of the patella includes three primary parts: the medial, intermediate, and lateral facets. Each facet plays a unique role during locomotion and contributes to the range of motion available in the stifle joint. Knowledge of this anatomy can help in diagnosing and treating stifle injuries and conditions. Proper functioning of the patella also prevents potential soft tissue injuries, thereby promoting longevity in a horse’s athletic career. Therefore, understanding the equine patella is essential for those involved in equine sports and healthcare.
Pathologies of the Equine Patella
Pathologies of the equine patella can significantly affect a horse’s mobility and performance. Common issues include patellar luxation and arthritis within the stifle joint. Patellar luxation occurs when the patella displaces from its normal position, leading to pain and an unstable stifle. This condition can be congenital or acquired, often requiring veterinary intervention. Symptoms of luxation may include limping, difficulty flexing the leg, or a noticeable inability to perform simple tasks like turning. Arthritis, on the other hand, is a degenerative condition that affects both the patella and surrounding joints. This condition often results from wear and tear over time or past injuries. The signs of arthritis include stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. Regular assessments of the horse’s movement can help catch these problems early, improving prognosis and treatment outcomes. Preventative care, such as maintaining a proper diet, regular exercise, and sufficient warm-up routines, can help protect the patella from injury and degeneration. Understanding how to manage these conditions can ensure your horse remains healthy and active throughout its life.
The anatomical relationship between the patella and surrounding structures plays an essential role in a horse’s overall biomechanics. The patellar ligament, which connects the patella to the tibia, also provides critical support during movement. When the quadriceps muscles contract, the tension in the patellar ligament stabilizes the joint, enabling effective force transfer between limbs. Proper anatomy allows the horse to absorb impacts during high-speed activities, reducing the risk of injury. Maintaining this anatomical relationship is vital in rehabilitation and recovery scenarios. Physiotherapists often emphasize strengthening the muscles surrounding the patella to enhance support and stability. Regularly incorporating exercises that target the quadriceps can help maintain optimal function. Furthermore, understanding the biomechanics of the patella aids in selecting appropriate equipment, such as saddles or leg wraps, tailored to the horse’s unique anatomy. An awareness of how the patella interacts with other structures can also guide effective training regimens that minimize stress and strain. Healthy patellar function allows for more powerful strides and minimizes the risk of chronic lameness, ensuring the horse can reach its full performance potential.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
The path to recovery from patellar injuries requires a comprehensive understanding of the equine patella’s anatomy and function. Rehabilitation strategies should incorporate exercises that focus on gradually increasing range of motion while minimizing stress on the stifle. Targeted exercises may include walking on varied terrains or controlled trotting under supervision. The goal is to strengthen the muscles around the patella without overexerting the joint. Knowing the nuances of a horse’s anatomy allows trainers and caretakers to create individualized rehabilitation protocols. Working closely with a veterinarian ensures that the recovery plan aligns with the equine athlete’s unique needs. Additional therapies, such as ultrasound or laser treatments, can enhance recovery by promoting circulation and minimizing inflammation. Furthermore, nutritional considerations play a vital role in recovery. Adequate proteins, omega fatty acids, and anti-inflammatory supplements can support healing processes. Monitoring the horse’s response to rehabilitation exercises provides insights on progression and adaptations required along the way. Ensuring proper recovery helps prevent future complications, thereby maintaining the horse’s active lifestyle and athletic integrity over the long term.
In conclusion, understanding the equine patella’s anatomy, function, and potential issues is critical for any person involved with horses. This knowledge can significantly impact not only performance but also injury prevention and rehabilitation. Horse owners are encouraged to become familiar with the signs of patellar dysfunction and to stay informed about best practices for maintaining joint health. Building a strong foundation of muscle around the stifle, employing preventive care routines, and tracking changes in mobility are all crucial steps in equine management. Additionally, regular veterinary check-ups can ensure ongoing health monitoring. This vigilance enables timely responses to any arising issues, promoting long-term athleticism for the horse. As horses continue to perform in a variety of equine sports, their anatomical considerations will remain pivotal for optimal care. The equine patella, while small in size, plays a substantial role in ensuring that these animals thrive in their endeavors. Thus, investing time in understanding this complex joint structure can greatly benefit horses and their riders or caregivers in achieving their goals together.
Future Studies and Research
Future studies on the equine patella promise to expand our understanding of this critical anatomical structure. Ongoing research into the biomechanics of equine movement will yield new insights into how we can optimize performance and health. For instance, examining different breeds and their predisposition to patellar injuries can inform breeding practices aimed at enhancing athletic capability. Additionally, advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, will aid in diagnosing complex patellar pathologies more accurately. This could revolutionize treatment protocols and rehabilitation strategies. Understanding the variations in patellar morphology across breeds could lead to more tailored approaches in veterinary medicine. Researchers are also focusing on the environmental factors influencing joint health. Investigating the impacts of nutrition, exercise regimes, and workload can augment current knowledge. Such studies aim to establish guidelines that help maintain patellar functions, contributing to the overall well-being of the horse. Integrating knowledge from diverse fields toward equine anatomy will continuously enhance how we care for these magnificent animals. Thus, the equine patella serves as a vital point of focus, prompting ongoing dialogue and exploration in the equine community.
The equine patella is a vital component of equine anatomy, integral to the horse’s locomotion and health. By understanding its function, associated conditions, and rehabilitation, we can better serve horses throughout their lives, ensuring performance and well-being.