Understanding the Role of the Posterior Chain in Powerlifting
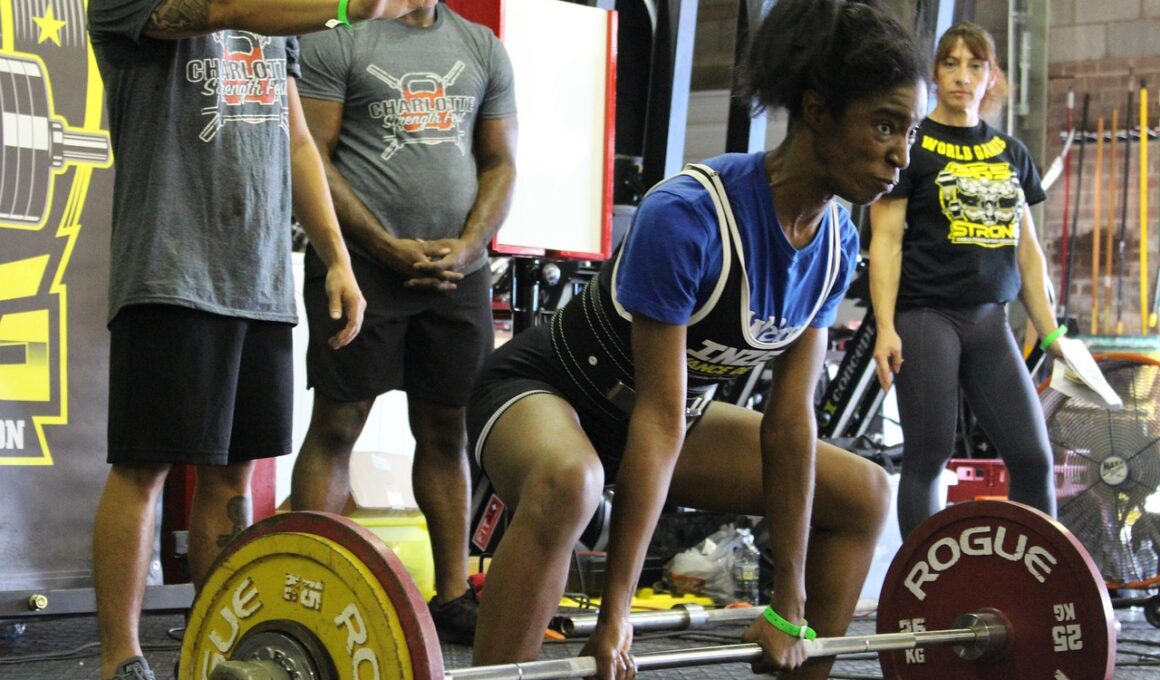
The posterior chain refers to a group of muscles located on the backside of the body, including the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. In powerlifting, these muscles play a crucial role, particularly in the performance of the deadlift and squat. Strong posterior chain muscles enhance an athlete’s ability to lift heavier weights and maintain optimal form throughout these movements. By targeting these areas during training, powerlifters can improve their overall strength, stability, and power. The posterior chain not only contributes to lifting performance but also aids in injury prevention, as strong muscles support the spine and pelvis. Many lifters, however, often neglect these muscles, resulting in imbalances that can hamper strength gains and lead to injuries. To address this, it’s essential to incorporate specific exercises that target the posterior chain into a powerlifting training routine. In the following sections, we will explore various techniques to strengthen these crucial muscles and understand how they influence overall performance in powerlifting competitions.
The Importance of the Hamstrings
The hamstrings are a key component of the posterior chain, playing an essential role in knee flexion and hip extension, both of which are vital for powerlifters. They assist in creating the force necessary to lift weights in the squat and deadlift. Additionally, strong hamstrings help prevent common injuries related to muscle strain. When the hamstrings are weak or underdeveloped, the risk of injury increases, particularly in the lower back, as other muscles compensate for the lack of strength. Moreover, neglected hamstrings can lead to poor lifting mechanics and inefficient movements. Incorporating exercises such as Romanian deadlifts, hamstring curls, and good mornings is essential to developing hamstring strength. These exercises not only strengthen the hamstrings but also enhance overall posterior chain functionality, thereby improving performance. Engaging in regular hamstring training helps maintain muscular balance, which is critical for avoiding injuries and optimizing lifts. Ultimately, powerlifters aiming for peak performance must prioritize hamstring strength within their training regimen. By focusing on this aspect, they can boost their overall capability in the sport, achieving greater success in competitions.
The Role of the Glutes
The gluteal muscles are another critical component of the posterior chain, being crucial for stabilization and power generation during lifts. Strong glutes enhance hip extension, which is essential for performing squats and deadlifts effectively. When lifters activate their glutes effectively, they can generate significant force to propel the weight upward, leading to improved performance. Furthermore, well-developed glutes help with maintaining proper form, reducing the risk of injury caused by poor mechanics. Many powerlifters may experience difficulties achieving maximal strength due to underdeveloped glute muscles. Thus, it is imperative to assess and improve glute strength through targeted exercises. Movements such as glute bridges, hip thrusts, and squat variations can significantly enhance glute recruitment and strength. Regularly incorporating these exercises into training can lead to remarkable improvements in overall strength, explosiveness, and performance. Additionally, well-developed glutes contribute to maintaining pelvic stability, which is vital during heavy lifts. Overall, prioritizing glute training within the powerlifting context can lead to substantial benefits and successes on the competition floor.
Lower Back Strength and Stability
The lower back, comprising the lumbar spine and surrounding musculature, is an essential part of the posterior chain that significantly affects powerlifting performance. A strong lower back provides the necessary support during heavy lifts by maintaining an optimal lift position and safeguarding against injury. Weakness in this area can lead to improper form, muscle imbalances, and increased risk of injury, particularly to the spinal column. Therefore, training the lower back is paramount for maximizing performance in powerlifting. Effective exercises such as deadlifts, back extensions, and good mornings help build lower back strength and endurance. Emphasizing lower back workouts enhances not only strength but also the overall stability of the entire posterior chain. Powerlifters should focus on exercises that promote muscle engagement in their lower back to ensure adequate support during lifts. Ideally, incorporating lower back training into a powerlifting regimen should be balanced with overall body conditioning to avoid lopsided strength development. Strengthening this part of the posterior chain optimizes lift efficiency and minimizes injury potential over time.
Common Exercises for Strengthening the Posterior Chain
In order to effectively enhance the strength of the posterior chain, it is important to include specific exercises in training routines. Key exercises that should be considered include deadlifts, glute bridges, Romanian deadlifts, hip thrusts, back extensions, and kettlebell swings. Each of these movements targets different muscles within the posterior chain, contributing to overall strength and stability. Deadlifts primarily engage the hamstrings and lower back, whereas glute bridges emphasize glute activation and strength. Romanian deadlifts also boost hamstring and glute strength, important for squats and the deadlift. Hip thrusts focus on building powerful glutes, which can considerably improve lifting capability. Back extensions foster lower back development, crucial for maintaining proper lifting mechanics. Incorporating kettlebell swings not only aids in conditioning but also promotes explosive hip extension, benefiting overall lifting potential. Furthermore, consistency in performing these exercises will yield noticeable strength gains. By integrating these movements into a comprehensive powerlifting program, athletes will likely see meaningful improvements in lifts, thus elevating their overall performance.
The Impact of Mobility on Posterior Chain Strength
Mobility plays a vital role in optimizing posterior chain strength and overall performance in powerlifting. Athletes often find that limited range of motion can hinder the effectiveness of exercises targeting the posterior chain. Addressing mobility issues can allow powerlifters to achieve better lifting positions, which translates directly into improved performance. Incorporating dynamic stretching and mobility exercises for the hips, hamstrings, and lower back is essential for ensuring optimal movement patterns. Examples include hip openers, hamstring stretches, and lower back rotations. Additionally, foam rolling can alleviate tension in tight muscles, fostering better flexibility and mobility. Powerlifters should dedicate time to mobility work in every training session to maximize gains from their strength training efforts. Improved mobility not only enhances lift performance but also contributes to injury prevention by promoting a balanced and functional posterior chain. By prioritizing mobility within their regimen, powerlifters can ensure they are training the posterior chain effectively. As a result, developing better mobility leads to greater strength potential and overall success in powerlifting competitions.
Conclusion: Training the Posterior Chain
In conclusion, training the posterior chain is crucial for powerlifters aiming for peak performance. By focusing on strengthening the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back, athletes can enhance their overall lifting capability and reduce the risk of injury. Incorporating targeted exercises such as deadlifts, glute bridges, and back extensions can significantly improve strength and stability in these critical areas. It is essential to note that consistency and progressive overload play vital roles in achieving desired results. Moreover, addressing mobility ensures optimal movement patterns, further benefiting overall lift performance. Powerlifters must remember that neglecting the posterior chain can lead to imbalances, decreased strength output, and increased injury risk. Therefore, integrating comprehensive posterior chain training into their programs will foster improved strength and mechanics. By dedicating adequate attention to this crucial aspect of their training, powerlifters can achieve their goals, maximize lifting potential, and excel in competitions. As lifters continue to develop their posterior chain strength, they will learn how vital it is to overall powerlifting success, and how it can ultimately shape their performance for the better.
Additional Tips for Posterior Chain Development
Beyond the key exercises outlined, there are additional considerations in developing the posterior chain for powerlifting. First, ensuring proper form during each lift is paramount; poor technique can negate the benefits of even the best training. Lifters should utilize mirrors, video feedback, or coaching to monitor and correct form as necessary. Secondly, varying the workouts to include different angles and movements can enhance overall muscle development and prevent adaptation. To keep the posterior chain growing, powerlifters could experiment with resistance bands, chains, or different foot placements to target muscles creatively. Nutrition also plays a significant role in muscle development; consuming adequate protein and quality carbohydrates supports recovery and overall growth. Lifters should prioritize a balanced diet, leveraging whole foods to fuel their training. Furthermore, sufficient rest and recovery enable muscles to repair and grow stronger, ensuring effective adaptation to stressful training. These additional tips can further enhance the effectiveness of a powerlifting program centered on posterior chain development. Ultimately, achieving the desired strength will require a multifaceted approach, encompassing exercise, nutrition, and rest, resulting in improved performance in powerlifting endeavors.