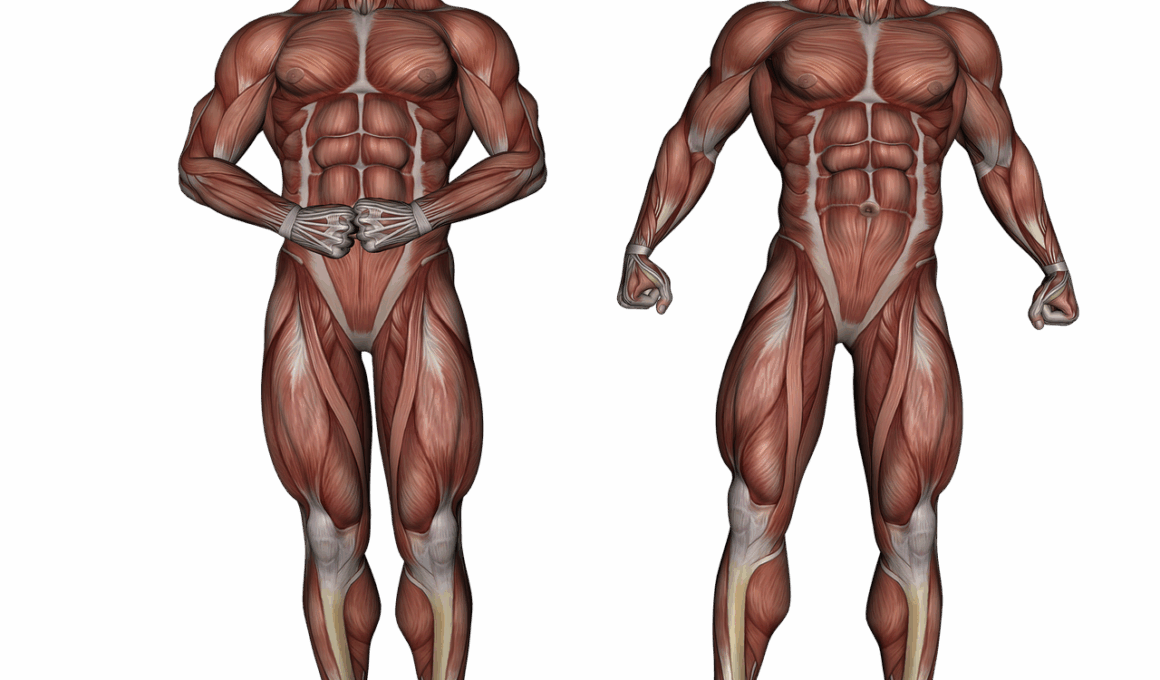
Injury Prevention Through Anatomical Awareness
Bodybuilding is a discipline that requires commitment, dedication, and most importantly, an understanding of the body’s anatomy to prevent injuries. Knowledge of anatomical structures can assist bodybuilders in creating effective workout routines, maximizing muscle engagement, and understanding potential risks. By being aware of how muscles, tendons, and ligaments interact, you can develop a movement strategy that minimizes risk. For example, learning about your joints’ range of motion can lead to safer lifting techniques that avoid undue stress on vulnerable areas. Injury prevention is crucial for maintaining consistent training and avoiding setbacks. Emphasizing anatomical awareness not only benefits professional lifters but is essential for beginners. Moreover, this knowledge empowers bodybuilders to modify techniques according to their unique body mechanics. Whether you include flexibility training, adequate warm-ups, or specific movements that emphasize proper alignment, anatomical awareness plays a critical role. This approach will ultimately promote longevity in the sport. Consequently, entering the gym without this awareness is like driving a car without understanding the controls. Improving your anatomical knowledge will enhance performance and help develop a sustainable training plan that can lead to long-term results.
Understanding muscle groups is fundamental for injury prevention. Bodybuilders often organize their workouts around key muscle groups to ensure balanced development. This includes the chest, back, legs, arms, and core. Dividing workouts by muscle groups can prevent overuse injuries by allowing time for recovery between sessions. When training a specific muscle group, ensure you are aware of its anatomical function. For instance, the quadriceps muscles in your legs are crucial for squatting; however, improper technique can lead to knee injuries. Practicing controlled movements not only enhances muscle growth but also pays dividends in injury prevention. In addition to focusing on one muscle group, it’s vital to recognize how these groups interact during compound movements. Exercises like deadlifts and squats engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Therefore, knowledge of how various muscle connections work is key to sustaining strength. A well-rounded program includes variations to target different angles of the muscle and include stabilization exercises to build resilience. As you develop strength, maintain flexibility and mobility to support these workouts. The ultimate goal is to cultivate overall body awareness that prioritizes health over sheer lifting volume. This approach is critical for safe longevity in bodybuilding.
The Role of Flexibility in Injury Prevention
Flexibility is another essential aspect of injury prevention. Many bodybuilders overlook flexibility training in their routines. However, maintaining supple muscles and joints ensures an optimal range of motion and prevents injuries. Integrating stretching routines can significantly improve flexibility. Flexibility training, such as dynamic stretching before workouts and static stretching afterward, enhances muscle elasticity. This not only benefits performance but ensures that muscles are prepared for lifting. When building muscles, tendons also adapt, but they need time to adjust to increased loads; hence proper stretching helps maintain alignment and function. Moreover, understanding the specific demands of modern bodybuilding can help you create a personalized stretching routine that addresses weaker links in your kinetic chain. Focusing on areas prone to tightness, such as the hamstrings or hip flexors, will pay dividends when lifting heavy weights. Bodybuilders should incorporate yoga or Pilates into their cross-training as well. This promotes body awareness, core strength, and flexibility. Properly balanced routines enhance both strength gains and health. Ultimately, a commitment to flexibility will help you lift more effectively while minimizing the chances of serious injuries throughout your bodybuilding journey.
Another aspect of anatomical awareness involves understanding biomechanical principles. Lifters must respect the mechanics of their movements to enhance performance and avoid injuries. For instance, the barbell squat is a foundational exercise that demonstrates the importance of biomechanics. Proper squat mechanics involve aligning knees, hips, and ankle joints. Misalignment can lead to strain on the knees and result in chronic pain. Additionally, performing squats with an improper stance can impede performance as well as raise the risk of injury. In terms of anatomy, the posterior chain (low back, glutes, and hamstrings) plays a critical role in overall power. Therefore, incorporating exercises targeting these muscles is important for injury prevention. Practicing movements like deadlifts strengthens the entire posterior chain, enhancing their stability and function. By increasing the strength of these crucial muscle groups in relation to your overall strength profile, you can reduce injury risks significantly. This added stability will enhance your performance across various lifts. Always integrate anatomical knowledge into program design and execution to mitigate injury risks. Understanding body mechanics and applying these principles to workouts ultimately leads to optimized performance in bodybuilding and reduced chances of injury.
Importance of Proper Recovery Techniques
Proper recovery is crucial for injury prevention in bodybuilding. Many athletes often underestimate its significance amid rigorous training schedules. Recovery not only allows muscles to repair but also helps align and reset the body’s mechanisms. Essential recovery practices include adequate sleep, nutrition, and active recovery sessions. Sleep is vital, and chronic sleep deprivation directly affects muscle recovery. Incorporating quality rest days into your training regimen allows the body to heal and prevents overtraining. Similarly, nutrition plays a significant role in recovery. Consuming adequate quantities of protein, carbohydrates, and fats supports muscle rebuilding after rigorous workouts. Moreover, anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids can aid recovery. Over time, understanding personal nutrition needs will significantly impact your progress in bodybuilding. Active recovery days can also promote blood flow and prevent stiffness. Lighter activities such as walking or swimming can be effective supplements. Engaging in low-impact movements also helps maintain cardiovascular fitness during these periods. The commitment to nurturing your body through recovery techniques cannot be overstated. By addressing recovery, bodybuilders can prevent injuries while simultaneously enhancing muscle growth and performance in the long run.
Listening to your body is an essential practice for bodybuilding. Identifying differences between fatigue, soreness, and pain is critical. Each can indicate how you push yourself during training, but pain often signifies an underlying issue. Acknowledging when you need to rest or adjust your routine is vital for long-term success. Overexertion can lead to the development of chronic injuries affecting progress and mental enthusiasm. Body awareness involves recognizing signals such as discomfort, tightness, or limited ranges of motion. It’s important to consult with professionals like trainers or physiotherapists when faced with injuries or discomfort. They can provide personalized advice tailored to your goals. This approach fosters a better understanding of your limits and the types of variations that benefit your training regimen. Evaluating intensity and modifying exercise can minimize risks. Tune in to your body’s feedback and fine-tune exercises according to individual needs. Each session is an opportunity for growth, so prioritizing recovery and listening to bodily cues can enhance your journey in bodybuilding. Honoring your limits ensures that you can progress safely and sustainably throughout the phases of your training.
Conclusion: Embrace Anatomical Knowledge
Your path in bodybuilding will significantly benefit from a comprehensive understanding of anatomical knowledge. This awareness not only helps prevent injuries but enhances performance and overall training efficacy. As you embrace these principles, consider focusing on muscle group dynamics, biomechanics, flexibility, and recovery techniques. Coupling this information with a personalized workout regimen will help you achieve your fitness goals while promoting longevity in the sport. Committing to anatomical education will empower you as an informed lifter, leading to optimal health outcomes and successful progress. Integrating body awareness into the training process creates a sustainable pathway for development. Bodybuilding isn’t merely about lifting weights; it’s about understanding and caring for your body as a powerful tool for achieving success. The synthesis of intention, knowledge, and action is always crucial. Ultimately, by cultivating an anatomical awareness, you position yourself to thrive while minimizing injury risks. This foundational understanding will elevate your practice as you embrace bodybuilding as a lifelong journey. Make informed decisions, embrace best practices, and promote health as you pursue amazing transformations.
In summary, prioritizing anatomical awareness within bodybuilding is essential for injury prevention and overall effectiveness. Through proper understanding of the muscles, biomechanics, flexibility practices, and recovery strategies, bodybuilders can foster a safer training environment. Taking the time to embrace these principles will lead to enhanced performance, reduction in injury risks, and informed strategies for growth. Focusing on a balanced approach in all training regimes is paramount. As you navigate your bodybuilding journey, let anatomical knowledge be your guiding force. The muscles you train and how you train them tells the story of your dedication and resilience. Commit to this awareness and take proactive steps towards a healthier, more sustainable bodybuilding practice.