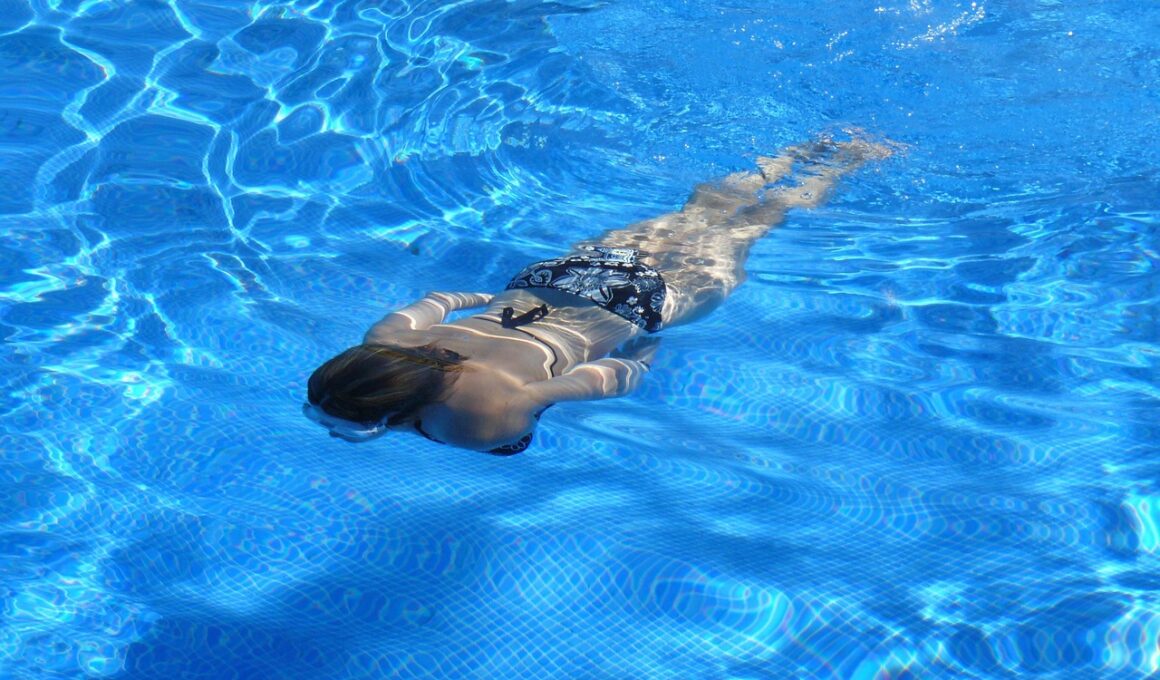
Understanding the Connection Between Swimming and Lung Function
Swimming is not only an enjoyable activity but also an effective exercise that enhances our respiratory health significantly. The rhythmic nature of swimming encourages deeper breathing, allowing more oxygen to enter the lungs. When we swim, the body adapts to different water pressures and temperatures which also stimulates lung function improvement. This adaptation can lead to a more efficient absorption of oxygen in the bloodstream, essential for overall health. Additionally, swimming often involves breath control techniques, promoting the expansion and strength of lung capacity. Athletes may engage in interval training or distance swimming, further benefiting their respiratory system. Swimming aids in clearing the airways by moistening the air, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with asthma or other respiratory ailments. Furthermore, the higher humidity of the pool environment helps in reducing respiratory symptoms. Many doctors recommend swimming for patients who suffer from such diseases. The connection between swimming and enhanced lung function is profound, indicating the need for aquatic activities in our daily routines to maintain healthy lungs. Incorporating swimming as a regular exercise can yield long-term benefits for respiratory health.
The Benefits of Swimming for Respiratory Health
One of the primary benefits of swimming is its remarkable ability to improve lung health. When you swim, your lungs increase their capacity through forced exhalation and inhalation. Each stroke involves careful timing of breath, which leads to enhanced lung volume. Improved lung volume helps the body work more effectively, ensuring that each cell receives enough oxygen during strenuous activities. Besides improving lung function, swimming can also help reduce stress on the respiratory system, as it requires less physical exertion compared to many other forms of exercise. As a non-impact sport, swimming minimizes stress on the joints and the respiratory tract. This makes it particularly suitable for elderly individuals or those recovering from injuries. Additionally, studies show that swimming can stimulate the production of surfactant, a substance crucial for lowering surface tension within the lungs. This surfactant production is essential for keeping the air sacs, or alveoli, open and functioning. Swimming can also improve attitudes toward physical exercise, leading to healthier lifestyle choices that yield long-lasting respiratory benefits, promoting better overall health outcomes over time.
Individuals suffering from conditions like asthma can especially benefit from regular swimming sessions. The practice allows for controlled breathing, which can be crucial in managing asthma symptoms effectively. Unlike running or cycling, swimming is less likely to trigger an asthma attack due to the humid environment. Moreover, the act of swimming helps individuals focus on their breath, leading to improved respiratory control. Incorporating swimming into an asthmatic’s routine can lead to fewer exacerbations and improved overall lung function. It is often recommended for asthma sufferers to swim in heated pools, as warm air can assist in keeping airways open and relaxed. With the right precautions in place, swimming can be a safe and enjoyable form of exercise. Many asthma patients have successfully improved their lung capacity and overall respiratory endurance through consistent swimming. Additionally, the cardiovascular endurance gained from swimming can lead to enhanced overall fitness. Building lung capacity through swimming will also translate into better function during other exercise forms. Patients should consult their healthcare providers before starting any new exercise, assuring that swimming is the correct fit for their individual needs.
Breath Control and Lung Function
Mastering breath control is vital not only for swimming success but also for improving lung health. Techniques like bilateral breathing promote enhanced oxygenation and control over breath patterns. These methods help swimmers manage their breathing rhythmically while engaging in intense physical activity. Learning to time your breaths while swimming leads to longer intervals between inhalations and exhalations, ultimately increasing lung capacity over time. As swimmers become more proficient in their breath control, they also often notice prolonged underwater performance without discomfort. This can translate into greater endurance and reduced breathlessness when engaging in other physical activities. Furthermore, practicing breath control can assist with relaxation and stress management. The calming effects of swimming combined with attentive breathwork can contribute to better overall mental and physical health. Those who engage regularly in rhythmic breathing during their swims may also experience lower anxiety levels, which can greatly benefit lung function. Coaches often emphasize the importance of integrating breath control into swim training, driving awareness surrounding its potential health benefits. Ultimately, attempts to improve breath control should consistently focus on enhancing lung function, leading to a more rewarding swimming experience.
In addition to individual benefits, swimming also presents broader advantages for lung health in communities. Public swimming facilities often host programs that encourage participation from individuals of all ages, promoting health awareness. Community swimming lessons contribute to building confidence in the water while also educating participants on breath control techniques that can enhance lung function. Diverse swimming programs also cater to aquatic therapy sessions for individuals with respiratory issues, creating supportive environments for healing and wellness. Residents benefit from inclusive health initiatives that not only boost respiratory fitness but also foster social connections among community members. These communal efforts can lead to increased awareness about the importance of respiratory health and the effectiveness of swimming as a beneficial exercise form. Additionally, directly engaging in swimming can strengthen community ties further emphasizing the shared value of health. Everyone can enjoy swimming while improving their lung health, highlighting an engaging method to inspire physical activity. Initiatives aimed at increasing community swim participation can lead to healthier, happier populations by focusing on vital lung health benefits associated with swimming.
Final Thoughts on Swimming and Lung Health
Understanding the connection between swimming and lung function highlights essential health benefits for individuals. Engaging in aquatic activities regularly can significantly improve overall respiratory health, leading to better lung capacity and function. Swimming is an accessible and effective form of exercise that many can enjoy, irrespective of their fitness level. As more researchers delve into the dynamics of swimming and lung function, exciting findings point toward long-term respiratory health improvements. With education and awareness, individuals can adopt swimming to foster better health outcomes. Regardless of age or fitness level, benefiting from swimming exercises can be within reach. It is crucial that people interested in enhancing their lung health through swimming approach the activity with an informed mindset. Incorporating lessons about proper techniques, breath control, and aquatic safety can help achieve the benefits swimming offers. Furthermore, community engagement fosters a supportive and encouraging atmosphere for those looking to embark on this journey. Swimmers across the globe continue to discover the advantages of enhanced respiratory function while participating in an activity they love. Ultimately, embracing swimming as an outlet for health leads to transformative changes in lung well-being.
In summary, swimming plays a crucial role in promoting respiratory health. The activity not only supports lung function but also creates a diversely engaging community context. The long-term benefits of swimming for individuals include increased lung capacity, improved breath control, and stronger respiratory endurance. Whether for those with chronic health conditions or the general population, incorporating swimming into one’s routine can yield notable benefits. Consequently, as more individuals seek enjoyable and effective ways to enhance their physical fitness, swimming stands out as a compelling option. While the advantages of swimming are multifaceted, the connection with lung health deserves special emphasis. Those motivated to experience the positive effects of swimming should actively pursue the opportunity and engage with local programs designed to support health goals. In doing so, they contribute to a healthier lifestyle while enjoying a low-impact and versatile exercise form. The benefits of swimming extend beyond the individual to encompass community wellness as well. As aquatic environments promote inviting spaces for health-related initiatives, swimming fosters not just physical benefits but holistic well-being too. Ultimately, embracing swimming as a favorable health strategy can lead to lasting improvements in respiratory health.